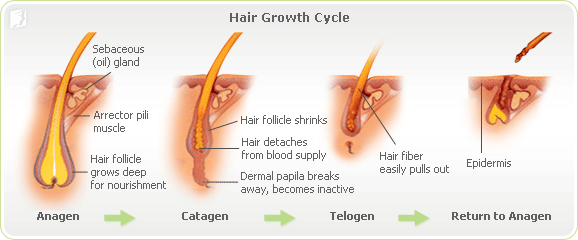
About 90% of the hair on a person’s scalp is growing at any one time. The growth phase lasts between two and six years. Ten percent of hair is in a resting phase that lasts 2-3 months. Hair is shed at the end of the resting phase. When hair is shed, new hair from the same follicle replaces it and the growing cycle starts again. Scalp hair grows at a rate of about 1/2 inch per month. As people age, rate of hair growth slows. Natural blondes typically have more hair than brunettes or redheads. It is normal to lose 50-100 hairs per day.
Causes of Excessive Hair Loss
Improper Hair Cosmetic Use/Improper Hair Care
- Improper use of chemical treatments on hair
- Hairstyles that pull on hair (ponytails, braids) that are too tight
- Shampooing, combing and brushing too often
- Vigorous handling of hair while wet
Hereditary Thinning or Balding
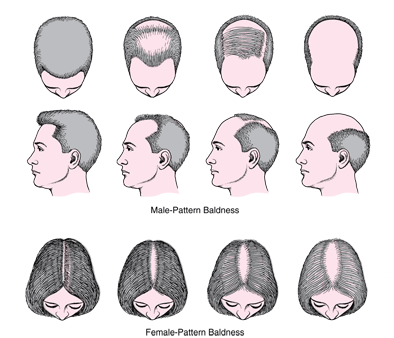
- Most common cause of hair loss
- Women with this trait develop thinning hair but do not become completely bald
- Hereditary thinning or balding is called androgenic (male) and pseudoandrogenic (female) alopecia
- Can begin in teens, twenties or thirties
- There is no cure, but treatment may help
Alopecia Areata
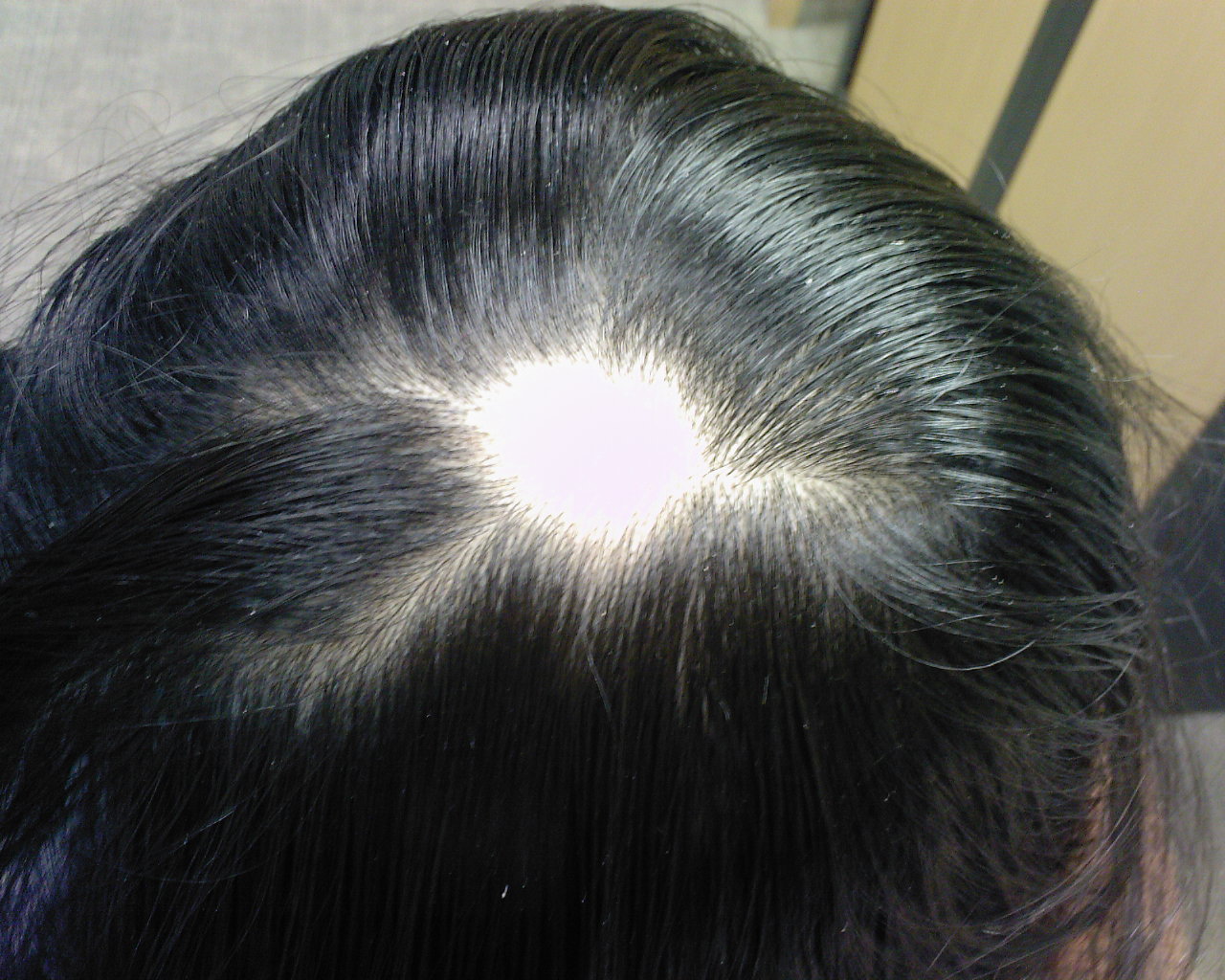
- The cause is unknown, but it is though to be autoimmune
- Hair falls out and results in totally smooth round patches on the scalp
- Hair can regrow without treatment but there are treatments available to make it regrow faster.
Childbirth
- More hairs stimulated to grow during pregnancy
- Many hairs enter resting phase after birth of the baby
- Large amounts of hair is shed after about 2-3 months, lasting about 6 months
High Fever, Severe Infection, Severe Flu
- Illness can cause hair to go into the resting phase.
- This typically corrects itself
Thyroid Disease
- Overactive and underactive thyroid can contribute to hair loss
- Lab tests are used for diagnosis
Inadequate Protein in Diet
- Body saves protein by shifting growing hairs into the resting phase
- Reversed by correcting eating habits
Medications
- Gout medications
- Arthritis medications
- Medications for heart problems
- High blood pressure medications
- Blood thinners
- High doses of vitamin A
Cancer Treatments
- Some treatments cause hair cells to stop dividing
- Can lose up to 90% of scalp hair
- Will regrow after treatment ends
Birth Control Pills
- Most of the time this is in patients who will experience pseudoandrogenic alopecia
- Stopping medication will correct the problem
Low Iron
- Can be corrected by iron supplementation
Major Surgery/Chronic Illness/Stressful Event
- Increased hair shedding for 1-3 months after the event
- This can reverse itself but can go on indefinitely
Fungal Infection of the Scalp
- “Ringworm”
- Can result in broken hair
- Cured by oral medication
Hair Pulling
- Trichotillomania
- Typically from habit or stress