Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis
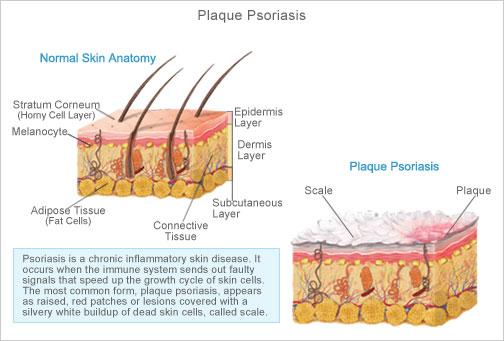
Psoriasis is an inflammatory skin condition that is typically chronic. It can vary from mild to very severe. It can be with or without joint pain.
Psoriasis is not contagious but can run in families.
Causes of Psoriasis
Exact cause is not known, but it is believed that the immune system plays a key role. The immune system activates T-cells (a type of white blood cell) and this causes the skin to grow too quickly. Skin typically replaces itself every 30 days, but in a person with psoriasis, the skin replaces itself about six times faster.
People typically have things that “trigger” psoriasis.
Common triggers:
- Stress
- Infection
- Certain Medications
- Cold, dry winter weather
- Lack of sunlight
- Injury – appears 10-14 days after
Types of Psoriasis
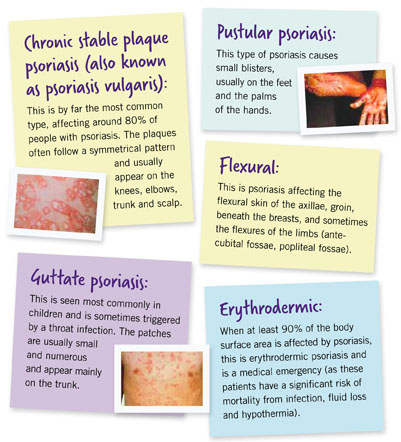
There are five major types of psoriasis:
- Plaque Psoriasis
Most common type. Appears as patches of raised, red skin with silvery white scale. They are typically on the elbows, knees, lower back and scalp.
- Guttate Psoriasis
These are small, red spots that usually affect children and young adults. Typically starts off as an infection.
- Pustular Psoriasis
White pustules surrounded by red skin. Typically on the palms and soles.
- Inverse Psoriasis
Smooth red lesions in skin folds.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis
Widespread redness with severe itching and pain. This can be life threatening.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis develops in 10-30% of people with psoriasis. This is typically chronic joint pain. Medication can prevent joint problems if started early. Without treatment, permanent degeneration can occur
Treatment of PsoriasisPsoriasis cannot be cured. Treatments can be very effective in controlling it, however.
Types of Treatment
- Topicals
- Light Therapy
- Systemic
- Biologic
Corticosteroids
Creams, ointments and lotions may clear the skin by reducing inflammation.
Calcipotriene
Form of vitamin D that controls growth of skin cells.
Coal Tar
Ultraviolet light slows rapid growth of skin cells
Methotrexate
This is an anti-cancer medication that can clear psoriasis. Regular blood tests are needed because of the effects of the medication on the liver.
Retinoids
This can cause dryness of the skin. It can be prescribed alone or in combination with UV light. Regular blood tests are needed.
Cyclosporine
This medication suppresses the immune system and is usually used to prevent organ rejection in patients who have received a transplant. Regular blood tests are needed.
These medications are typically given by injection or infusion. They are unique in that they pinpoint the exact part of the immune system that is involved with psoriasis.
There are many different biologic medications that may be used, given at different intervals.